Split Plot Analysis With Continuous Data
Split-Plot Designs
- Typically used in the case that you have two factors where one needs much larger units than the other.
Example:
A: 3 levels (large units)
B: 2 levels (small units)
- A and B levels are randomized into 4 blocks.
- But it differs from Randomized Block Designs. In each block, both have one of the 6 (3x2) treatment combinations. But Randomized Block Designs assign in each block randomly, while split-plot does not randomize this step.
- Moreover, because A needs to be applied in large units, factor A is applied only once in each block while B can be applied multiple times.
Hence, we have our model
If A is our factor of interest
\[ Y_{ij} = \mu + \rho_i + \alpha_j + e_{ij} \]
where
- i = replication (block or subject)
- j = level of Factor A
- \(\mu\) = overall mean
- \(\rho_i\) = variation due to the i-th block
- \(e_{ij} \sim N(0, \sigma^2_e)\) = whole plot error
If B is our factor of interest
\[ Y_{ijk} = \mu + \phi_{ij} + \beta_k + \epsilon_{ijk} \]
where
- \(\phi_{ij}\) = variation due to the ij-th main plot
- \(\beta_k\) = Factor B effect
- \(\epsilon_{ijk} \sim N(0, \sigma^2_\epsilon)\) = subplot error
- \(\phi_{ij} = \rho_i + \alpha_j + e_{ij}\)
Together, the split-plot model
\[ Y_{ijk} = \mu + \rho_i + \alpha_j + e_{ij} + \beta_k + (\alpha \beta)_{jk} + \epsilon_{ijk} \]
where
- i = replicate (blocks or subjects)
- j = level of factor A
- k = level of factor B
- \(\mu\) = overall mean
- \(\rho_i\) = effect of the block
- \(\alpha_j\) = main effect of factor A (fixed)
- \(e_{ij} = (\rho \alpha)_{ij}\) = block by factor A interaction (the whole plot error, random)
- \(\beta_k\) = main effect of factor B (fixed)
- \((\alpha \beta)_{jk}\) = interaction between factors A and B (fixed)
- \(\epsilon_{ijk}\) = subplot error (random)
We can approach sub-plot analysis based on
-
the ANOVA perspective
-
Whole plot comparisons
-
Compare factor A to the whole plot error (i.e., \(\alpha_j\) to \(e_{ij}\))
-
Compare the block to the whole plot error (i.e., \(\rho_i\) to \(e_{ij}\))
-
-
Sub-plot comparisons:
-
Compare factor B to the subplot error (\(\beta\) to \(\epsilon_{ijk}\))
-
Compare the AB interaction to the subplot error (\((\alpha \beta)_{jk}\) to \(\epsilon_{ijk}\))
-
-
-
the mixed model perspective
\[ \mathbf{Y = X \beta + Zb + \epsilon} \]
Application
Example 1
\[ y_{ijk} = \mu + i_i + v_j + (iv)_{ij} + f_k + \epsilon_{ijk} \]
where
- \(y_{ijk}\) = observed yield
- \(\mu\) = overall average yield
- \(i_i\) = irrigation effect
- \(v_j\) = variety effect
- \((iv)_{ij}\) = irrigation by variety interaction
- \(f_k\) = random field (block) effect
- \(\epsilon_{ijk}\) = residual
- because variety-field combination is only observed once, we can't have the random interaction effects between variety and field
library(ggplot2) data(irrigation, package = "faraway") summary(irrigation) #> field irrigation variety yield #> f1 :2 i1:4 v1:8 Min. :34.80 #> f2 :2 i2:4 v2:8 1st Qu.:37.60 #> f3 :2 i3:4 Median :40.15 #> f4 :2 i4:4 Mean :40.23 #> f5 :2 3rd Qu.:42.73 #> f6 :2 Max. :47.60 #> (Other):4 head(irrigation, 4) #> field irrigation variety yield #> 1 f1 i1 v1 35.4 #> 2 f1 i1 v2 37.9 #> 3 f2 i2 v1 36.7 #> 4 f2 i2 v2 38.2 ggplot(irrigation, aes( x = field, y = yield, shape = irrigation, color = variety )) + geom_point(size = 3) 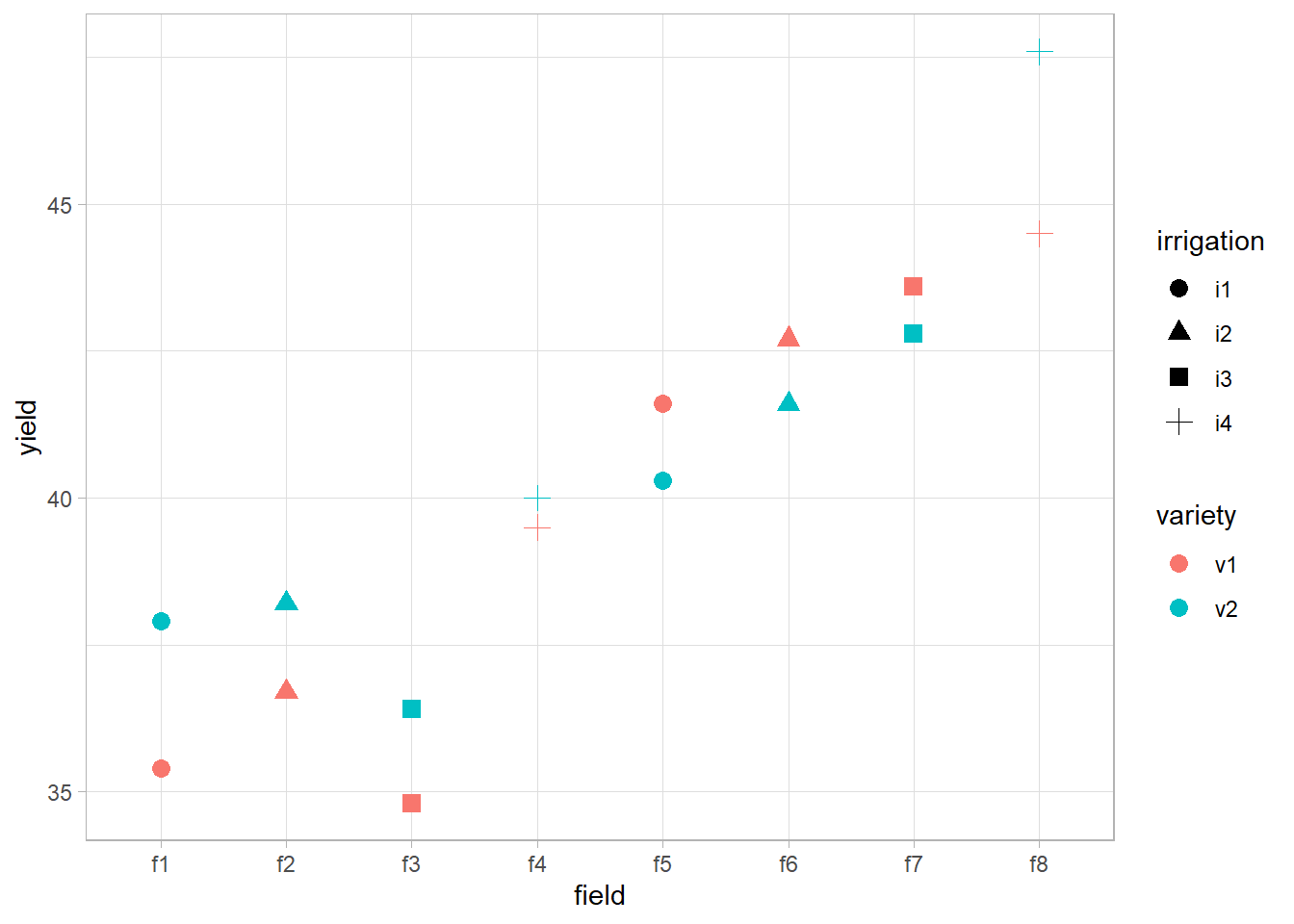
sp_model <- lmerTest:: lmer(yield ~ irrigation * variety + (1 | field), irrigation) summary(sp_model) #> Linear mixed model fit by REML. t-tests use Satterthwaite's method [ #> lmerModLmerTest] #> Formula: yield ~ irrigation * variety + (1 | field) #> Data: irrigation #> #> REML criterion at convergence: 45.4 #> #> Scaled residuals: #> Min 1Q Median 3Q Max #> -0.7448 -0.5509 0.0000 0.5509 0.7448 #> #> Random effects: #> Groups Name Variance Std.Dev. #> field (Intercept) 16.200 4.025 #> Residual 2.107 1.452 #> Number of obs: 16, groups: field, 8 #> #> Fixed effects: #> Estimate Std. Error df t value Pr(>|t|) #> (Intercept) 38.500 3.026 4.487 12.725 0.000109 *** #> irrigationi2 1.200 4.279 4.487 0.280 0.791591 #> irrigationi3 0.700 4.279 4.487 0.164 0.877156 #> irrigationi4 3.500 4.279 4.487 0.818 0.454584 #> varietyv2 0.600 1.452 4.000 0.413 0.700582 #> irrigationi2:varietyv2 -0.400 2.053 4.000 -0.195 0.855020 #> irrigationi3:varietyv2 -0.200 2.053 4.000 -0.097 0.927082 #> irrigationi4:varietyv2 1.200 2.053 4.000 0.584 0.590265 #> --- #> Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1 #> #> Correlation of Fixed Effects: #> (Intr) irrgt2 irrgt3 irrgt4 vrtyv2 irr2:2 irr3:2 #> irrigation2 -0.707 #> irrigation3 -0.707 0.500 #> irrigation4 -0.707 0.500 0.500 #> varietyv2 -0.240 0.170 0.170 0.170 #> irrgtn2:vr2 0.170 -0.240 -0.120 -0.120 -0.707 #> irrgtn3:vr2 0.170 -0.120 -0.240 -0.120 -0.707 0.500 #> irrgtn4:vr2 0.170 -0.120 -0.120 -0.240 -0.707 0.500 0.500 anova(sp_model,ddf = c("Kenward-Roger")) #> Type III Analysis of Variance Table with Kenward-Roger's method #> Sum Sq Mean Sq NumDF DenDF F value Pr(>F) #> irrigation 2.4545 0.81818 3 4 0.3882 0.7685 #> variety 2.2500 2.25000 1 4 1.0676 0.3599 #> irrigation:variety 1.5500 0.51667 3 4 0.2452 0.8612 Since p-value of the interaction term is insignificant, we consider fitting without it.
library(lme4) sp_model_additive <- lmer(yield ~ irrigation + variety + (1 | field), irrigation) anova(sp_model_additive,sp_model,ddf = "Kenward-Roger") #> Data: irrigation #> Models: #> sp_model_additive: yield ~ irrigation + variety + (1 | field) #> sp_model: yield ~ irrigation * variety + (1 | field) #> npar AIC BIC logLik deviance Chisq Df Pr(>Chisq) #> sp_model_additive 7 83.959 89.368 -34.980 69.959 #> sp_model 10 88.609 96.335 -34.305 68.609 1.3503 3 0.7172 Since p-value of Chi-square test is insignificant, we can't reject the additive model is already sufficient. Looking at AIC and BIC, we can also see that we would prefer the additive model
Random Effect Examination
exactRLRT test
- \(H_0\): Var(random effect) (i.e., \(\sigma^2\))= 0
- \(H_a\): Var(random effect) (i.e., \(\sigma^2\)) > 0
sp_model <- lme4:: lmer(yield ~ irrigation * variety + (1 | field), irrigation) library(RLRsim) exactRLRT(sp_model) #> #> simulated finite sample distribution of RLRT. #> #> (p-value based on 10000 simulated values) #> #> data: #> RLRT = 6.1118, p-value = 0.0103 Since the p-value is significant, we reject \(H_0\)
mccrackenmashe1968.blogspot.com
Source: https://bookdown.org/mike/data_analysis/split-plot-designs.html